Choosing between QR Codes vs Barcodes depends on whether you need simple item identification or complex, interactive data sharing. While barcodes have been the retail standard for decades, QR codes have revolutionized how businesses interact with customers through QR code scanning and mobile connectivity.
1. QR Codes vs Barcodes: What Is the Difference?
The fundamental difference lies in their dimensionality. Barcodes (1D) are linear and store data horizontally using parallel lines. In contrast, QR Codes (2D) are matrix-based, storing information both horizontally and vertically.

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Common Barcode Types and Their Uses
Barcodes for products are primarily used for simple identification linked to a central database.
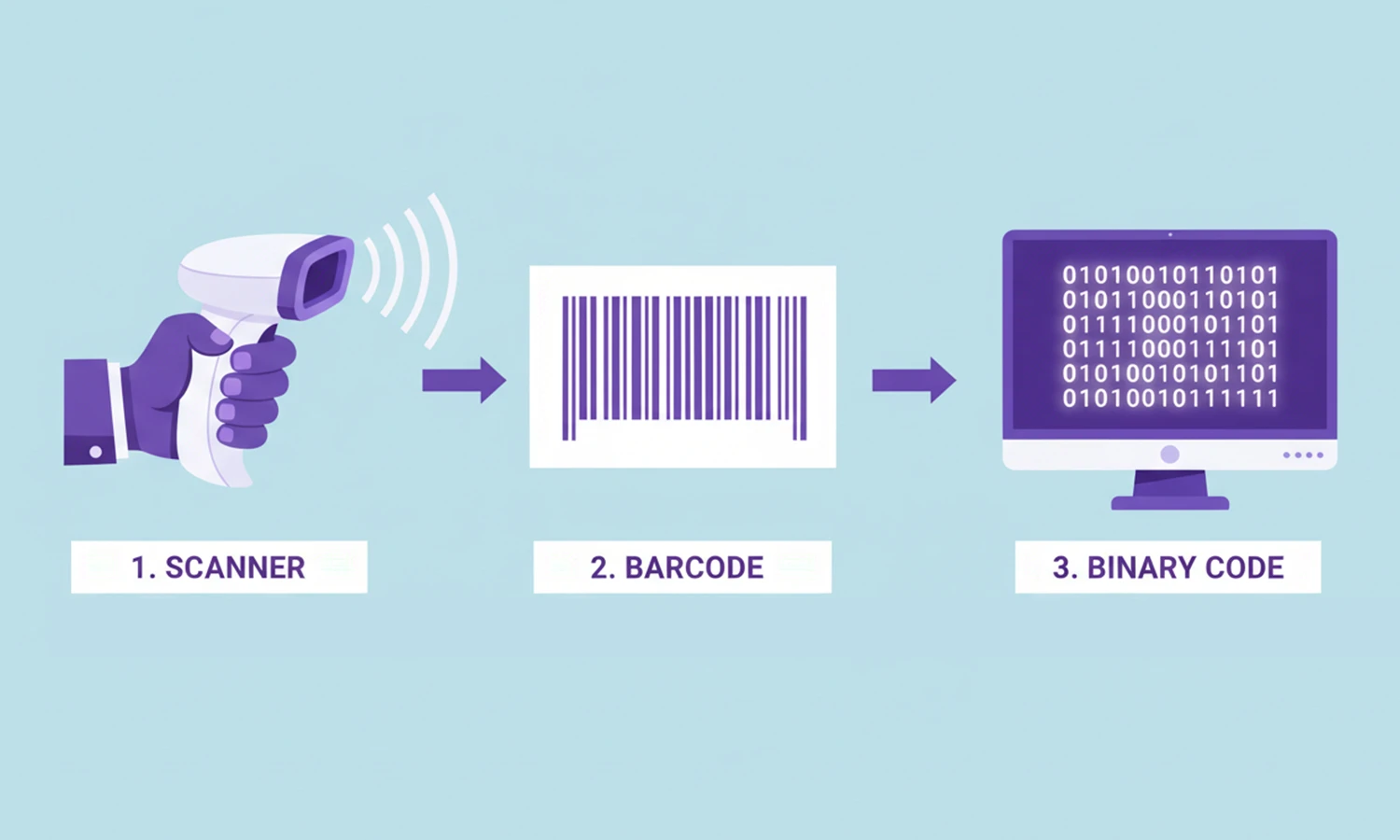
- UPC (Universal Product Code): The retail standard in North America for checkout.
- EAN (European Article Number): The international version of the UPC.
- Code 128: A high-density code used for shipping and logistics.
- ITF-14: Designed for printing on corrugated cardboard for warehouse pallets.
3. Common QR Code Types and Their Uses
QR codes for business are categorized by their technical structure and functionality.
- Micro QR Code: A compact version for space-constrained items like circuit boards.
- Static QR Codes: Best for permanent info like a home Wi-Fi password.
- Dynamic QR Codes: The gold standard for QR code for marketing. These allow you to change the destination link at any time via QR Dada without reprinting the code.
- vCard QR Codes: A modern qr code business card that saves contact info directly to a phone.
4. When to Use QR Codes or Barcodes
- Use Barcodes if: You are managing internal retail inventory or high-speed logistics using dedicated laser scanners.
- Use QR Codes if: You want smartphone compatibility, customer engagement, or the ability to update your content via QR Dada.
5. Why QR Codes Are Better Than Barcodes
There are several QR code benefits over barcodes that make them the superior choice for modern growth:
- Smartphone Compatibility: No special hardware is needed; anyone with a phone can scan.
- Superior Durability: Built-in error correction allows them to work even if dirty or damaged.
- Trackability: Using QR Dada, you can see real-time analytics like location and scan counts.
- Branding: Unlike barcodes, you can customize QR codes with logos and colors to match your brand identity.
6. How Much Data Can Each Code Store?
A standard barcode is limited to roughly 20–30 numeric characters. In comparison, a Version 40 QR code can store:
- Numeric only: 7,089 characters
- Alphanumeric: 4,296 characters
When using a platform like QR Dada, QR codes for business stay simple. By encoding a short redirect link instead of raw data, the pattern remains easy to scan while leading to unlimited digital content.
7. Which One Is More Secure?
- QR Codes: Superior for authentication because they support encrypted data strings. QR Dada also allows you to password-protect links.
- Barcodes: "Physically" safer from phishing because they cannot automatically trigger a website, but they are very easy to clone.
Key Takeaways
- Barcodes are best for high-speed, internal retail tracking.
- QR codes are essential for consumer engagement and QR code business card solutions.
- QR codes for business offer advanced tracking and editability that barcodes lack.
QR Dada is the ideal tool for creating professional, dynamic QR codes.


